Indirect Dataflow¶
This article introduces some SQL elements that generate indirect dataflow. Indirect dataflow usually is generated from columns used in the where clause, group by clause, aggregate function and etc.
RelationRows¶
In order to create indirect dataflow between columns, we introduce a pseudo column: RelationRows.
RelationRows is a pseudo column of a relation used to represents the number of rows in a relation. As its name indicates, RelationRows is not a real column in the relation(table/resultset and etc). Usually, It is used to represents a dataflow between a column and a relation.
RelationRows pseudo column can be used in both the source and target relation.
1 RelationsRows in target relation¶
Take this SQL for example:
1 2 3 | |
The total number of rows of the select list is impacted by the value of column sal in the where clause. So, an indirect dataflow is created like this:
1 | |
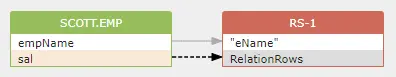
2 RelationRows in source relation¶
Here is another sample:
1 2 | |
The value of count() function and sum(sal) function is impacted by the number of rows in the scott.emp source table.
1 2 | |
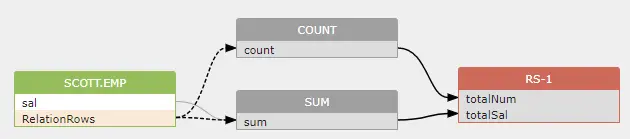
3. Table level dataflow using RelationRows¶
RelationRows is also used to represent table level dataflow.
1 | |
A table level dataflow is not built on a table, but on the pseudo column RelationRows like this:
1 | |
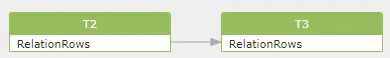
Build a table to table dataflow that using the RelationRows pseudo column for 2 reasons:
- This pseudo column that used to represent a table to column dataflow will be used to generate a table to table dataflow later if user need a table-level lineage model.
- If other columns in the same table are used in a column to column dataflow while this table itself is also in a table to table dataflow, then, this pseudo column will make it possible for a single table to includes both the column to column dataflow and table to table dataflow.
take this SQL for example
1 2 | |
The first create view statement will generate a column-level dataflow between the table t2 and view v1,
1 | |
while the second alter table statement will genereate a table-level dataflow between the table t2 and t3.
1 | |
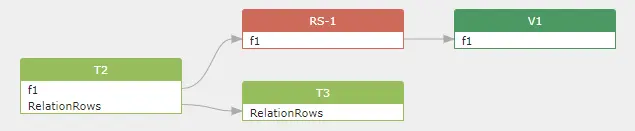
As you can see, Table t2 involved in the column to column dataflow generated by the create view statement, It also involved in a table to table dataflow generated by the alter table statement. A single table t2 in the above digram shows that it includes both the column to column dataflow and a table to table dataflow.
Where and Group-By¶
1. Columns in where clause¶
Some of the columns in source tables in WHERE clause do not influence target columns but are crucial for the selected row set, so they should be saved for impact analyses, with an indirect dataflow to the target tables.
Take this SQL for example:
1 2 3 | |
The total number of rows of the select list is impacted by the value of column sal in the where clause. We build an indirect dataflow for this relationship.
1 | |
.webp)
2. COUNT()¶
COUNT() function is an aggregate function that used to calculate the total number of rows of a relation.
2.1 where clause without group by clause¶
1 2 3 | |
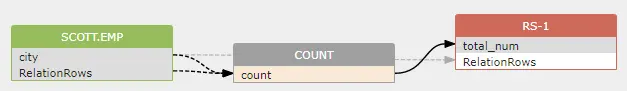
In above SQL, two indirect dataflows will be created, because the value of COUNT() is impacted by the city column in where clause and the total number of rows of scott.emp table.
1 2 | |
2.2 where clause with group by clause¶
1 2 3 4 | |
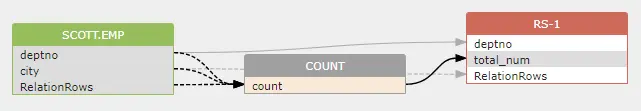
As you can see, besides the two indirect dataflows created in the previous SQL, a third indirect dataflow is created using the deptno in the group by clause.
1 2 3 | |
3. Other aggregate function¶
When creating indirect dataflow, other aggregate functions such as SUM() works a little bit differently to the COUNT() function.
3.1 where clause with group by clause¶
1 2 3 4 | |
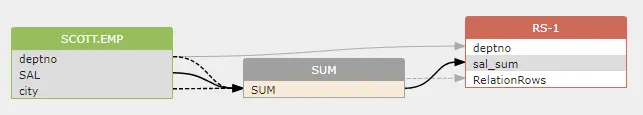
aggregate function such as SUM() calculates the value from a record set determined by the columns used in the group by clause, so deptno column in the group by clause is used to create an indirect dataflow to SUM() function.
an indirect dataflow is created from deptno to SUM().
1 | |
RelationRows pseudo column will not be used to create an indirect dataflow if group by clause if presented.
3.2 where clause without group by clause¶
1 2 3 | |
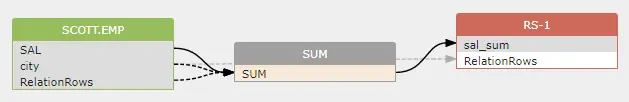
The above SQL means that the whole record set of the table will be used to calculate the value of SUM() function.
So two indirect dataflows will be created as below:
1 2 | |
4. Summary¶
- Columns in where clause always create an indirect dataflow to all aggregate functions used in the select list.
- RelationRows pseudo column always create an indirect dataflow to COUNT() function, but only create an indirect dataflow to other aggregate functions such as SUM() when the group by clause is not used.
- Columns in the group by clause always create an indirect dataflow to all aggregate functions used in the select list.
References¶
- xml code used in this article is generated by DataFlowAnalyzer tools
- digram used in this article is generated by the Gudu SQLFlow Cloud version